Business
Protect the poor from galloping inflation, World Bank advises Nigerian govt, others

… lowers Nigeria’s economic growth forecast
The World Bank has called on the Federal Government of Nigeria and other governments in the Sub-Saharan African region to urgently implement measures to restore macro-economic stability and protect the poor from the high inflation and current slow economic growth.
The World Bank has also lowered its economic growth forecast for Nigeria in 2023 to 3.2 per cent from 3.3 per cent due to the slowdown in global growth, the war in Ukraine and declining demand from China for commodities produced in Africa.
It projected that the Sub-Saharan African region would record a lower economic growth of 3.3 per cent in 2022 as against the 4.1 per cent recorded in 2021.
The forecasts were contained in the October edition of the World Bank’s Africa’s Pulse, a biannual analysis of the near-term regional macroeconomic outlook, and economic growth in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA).
Highlighting the growth factors for Nigeria’s economy, the World Bank said, “The Nigerian economy is projected to slow in 2023, down to 3.2 per cent (from 3.3 per cent) and persist at this level the following year. Growth will be supported mainly by the rebound in private consumption prompted mostly by accommodative monetary policy as inflationary pressures subside.
“Private consumption expenditure is forecast to decrease this year and grow next year. This performance will likely continue in 2024. On the production side, growth in 2023 will be supported by industry (with the growth of 5.1 per cent) with the mega-refinery project.”
On its growth forecast for the Sub-Saharan African region, the World Bank said: “Economic growth in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) is set to decelerate from 4.1% in 2021 to 3.3% in 2022, a downward revision of 0.3 percentage points since April’s Pulse forecast, mainly as a result of a slowdown in global growth, including flagging demand from China for commodities produced in Africa.
On the factors undermining economic growth in SSA, the World Bank said, “The war in Ukraine is exacerbating already high inflation and weighing on economic activity by depressing both business investments and household consumption. As of July 2022, 29 of 33 countries in SSA with available information had inflation rates over 5% while 17 countries had double-digit inflation.
“Elevated food prices are causing hardships with severe consequences in one of the world’s most food-insecure regions. Hunger has sharply increased in SSA in recent years driven by economic shocks, violence and conflict, and extreme weather. More than one in five people in Africa suffer from hunger and an estimated 140 million people faced acute food insecurity in 2022, up from 120 million people in 2021, according to the Global Report on Food Crises 2022 Mid-Year Update.
“The interconnected crises come at a time when the fiscal space required to mount effective government responses is all but gone. In many countries, public savings have been depleted by earlier programs to counter the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic, though resource-rich countries in some cases have benefited from high commodity prices and managed to improve their balance sheet.”
“Debt is projected to stay elevated at 58.6% of GDP in 2022 in SSA. African governments spent 16.5% of their revenues servicing external debt in 2021, up from less than 5% in 2010. Eight out of 38 IDA-eligible countries in the region are in debt distress, and 14 are at high risk of joining them. At the same time, high commercial borrowing costs make it difficult for countries to borrow on national and international markets while tightening global financial conditions are weakening currencies and increasing African countries’ external borrowing costs.”
Stressing the need for governments to improve the efficiency of existing resources and to optimize taxes in response to the above challenges, the World Bank added that, “In the agriculture and food sector, for example, governments have the opportunity to protect human capital and climate-proof food production by re-orienting their public spending away from poorly targeted subsidies toward nutrition-sensitive social protection programmes, irrigation works, and research and development are known to have high returns.”
Railway
Railway track vandalism: Urgent need for laws prohibiting scrap/metal picking to protect critical assets

Railway track vandalism: Urgent need for laws prohibiting scrap/metal picking to protect critical assets
By Onyedikachi Stanley Onovo
The wanton destruction and theft of Nigeria’s railway infrastructure and other critical public assets represent one of the gravest threats to national development and security.
Across the nation—from the Warri-Itakpe line to Abuja-Kaduna, the Eastern and Western Districts, Lagos-Ibadan, and throughout the Northern network—vandals systematically dismantle tracks, steal armoured cables, and pillage essential equipment. This crisis demands an immediate and robust legislative response.
The unending menace
The vandalism is perpetrated by a network of individuals, from local miscreants (“iron condemn”) to organised merchants who purchase and export stolen materials. Security reports and countless arrests underscore the scale of the problem:
In December 2023, a private security firm arrested 13 suspects for vandalising Abuja Mass Transit Rail assets. The suspects were said to be casual workers engaged by a Chinese company working on the railways, but said to have used the opportunity to steal the materials.
On June 2024, The Cable reported that the Nigerian Army arrested 47 suspected rail track vandals in Kaduna State.
In October 2025, police arrested a suspect vandalising railway electrical installations also in Kaduna State.
Radio Nigeria in December 2025 announced the arrest of three persons in Kwara State for vandalizing and stealing Railway clips and nuts in Offa.
In May 2021, TVC reported some individuals, including one Ejike Okeke were apprehended in Enugu with stolen sleepers and tracks.
On the 30th of January 2026 the Nigerian Television Authority reported that the NSCDC, Bauchi State Command arrested five suspects and intercepted a truck carrying vandalized railway tracks.
This relentless assault has plagued successive management of the Nigerian Railway Corporation (NRC), defying conventional counter-strategies.
A transformative leadership initiative
A pivotal shift began under the administration of President Bola Ahmed Tinubu with the appointment of Dr. Kayode Opeifa as Managing Director/CEO of the NRC.
Dr. Opeifa introduced a fundamental paradigm shift by redesignating what was carelessly termed “scrap” as “unserviceable critical national assets.”
This reframing has driven a transformative partnership with experts to manage these assets responsibly. The era of controversial public auctions—which often saw valuable national iron assets disappear, depriving Nigeria of materials for repurposing and industrialisation—is now over.
Today, a systematic process ensures these materials are reused or responsibly processed, with revenue reinvested into the Corporation. This home-grown solution is a commendable breakthrough that proves Nigerians can effectively solve national challenges.
The critical legislative gap: Targeting the market
While the NRC’s internal reforms are laudable, they alone cannot stem the tide. The root enabler of this vandalism is the thriving, unregulated market for stolen metal. To kill the vandal’s incentive, we must eradicate the demand.
Therefore, there is an urgent need for the National Assembly to enact legislation that:
1. Prohibits the buying and selling of any railway materials (serviceable or unserviceable) on the open market.
2. Imposes severe penalties on buyers and merchants of vandalised public assets, effectively targeting the economic drivers of this crime.
3. Mandates stringent federal regulation of all scrap metal dealers nationwide.
THE SCRAP DEALER NEXUS
The opaque operations of scrap dealers are a major concern. Their compounds are often shrouded, hiding the provenance of their materials. This unregulated space fuels not only railway vandalism but also community theft—from iron crossing bars in homes to street lamp holders.
Trailers loaded with questionable materials move freely from cities and expressways to unknown destinations. Without regulating this sector, our fight against vandalism remains superficial.
CONCLUSION
The partnership and innovation under Dr. Opeifa’s leadership at the NRC demonstrate what is possible with commitment and vision.
However, to secure our railways, power installations, and other critical assets, we must complement this institutional resolve with strong, deterrence-based law. Legislation that dismantles the market for stolen public property is not an option; it is a national imperative for Nigeria’s security and industrial future.
*Onyedikachi Stanley Onovo, Ph.D
FCAI, ANIPR
onyedikachionovo1@gmail.com excellentdikachi@yahoo.com
Auto
MOMAN, ALCMAN Partner BKG to Drive Nigeria’s Shift from Auto Imports to Industrial Production

MOMAN, ALCMAN Partner BKG to Drive Nigeria’s Shift from Auto Imports to Industrial Production
In what industry stakeholders view as a decisive move toward industrial rebirth, BKG Exhibitions Limited has entered into a strategic partnership with the Motorcycle Manufacturers Association of Nigeria (MOMAN) and the Automotive Local Content Manufacturers Association of Nigeria (ALCMAN) to accelerate local automotive manufacturing and reduce the country’s heavy reliance on imports.
The alliance, formalised in Lagos, signals a coordinated private-sector effort to reposition Nigeria’s automotive ecosystem from an import-dependent market to a production-driven industrial base capable of delivering value addition, technology transfer, and large-scale employment.
For decades, Nigeria’s automotive sector has been dominated by the importation of fully built vehicles and, more recently, the assembly of semi-knocked-down (SKD) and completely knocked-down (CKD) kits.
While these models generated commercial activity, stakeholders argue they failed to build deep industrial capacity or strengthen indigenous engineering expertise.
The new partnership seeks to change that narrative by transforming trade exhibitions into structured industrial platforms that connect manufacturers with policymakers, institutional buyers, investors, and international technical partners.
A senior executive at BKG Exhibitions said the collaboration represents a deliberate shift in strategy.
“Exhibitions must go beyond passive marketplaces. They must become engines of economic transformation where Nigerian manufacturers secure contracts, attract capital, and demonstrate production competence,” he said, noting that Nigeria already possesses strong demand but lacks a coordinated ecosystem to convert that demand into domestic output.
“Nigeria remains one of Africa’s largest mobility markets, driven by rapid urbanisation, a growing youth population, and expanding last-mile logistics services.
“Motorcycles and tricycles play a critical role in urban transport, agriculture distribution, and the fast-growing delivery economy.
“However, a substantial portion of these vehicles and their components are imported, placing pressure on foreign exchange and limiting domestic industrial growth.”
MOMAN President Rev. Lambert Ekewuba emphasized that strengthening local production would go beyond import substitution.
“When we manufacture locally, we create jobs, retain capital, and build the technical foundation for advanced automotive engineering,” he said.
ALCMAN Chairman, Chief Anselm Ilekuba, stressed the importance of developing a resilient components ecosystem, describing it as the backbone of any successful automotive industry.
“No country becomes an automotive powerhouse without first nurturing strong supplier networks. Nigeria must empower small and medium-scale enterprises producing metal parts, plastics, electrical systems, and other inputs,” he said.
Under the alliance, future exhibitions will feature dedicated pavilions showcasing Nigerian-made components and vehicles, offering manufacturers direct access to government agencies, transport operators, and regional distributors.
Analysts believe such curated exposure could gradually shift procurement patterns toward locally produced alternatives.
Beyond the domestic market, the partnership aims to position Nigeria as a manufacturing hub serving West and Central Africa, leveraging opportunities under the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA).
Industry leaders say expanding export capacity will depend on strengthening standards, financing mechanisms, and technical capability.
The alliance also plans coordinated advocacy for policies that support localisation, including improved access to financing, reduced duties on industrial machinery, technical training aligned with modern production systems, and procurement frameworks favouring locally manufactured goods.
Economists argue that a revitalised automotive manufacturing base could stimulate growth across steel, petrochemicals, logistics, warehousing, and tooling industries, reinforcing the sector’s role as a catalyst for broader industrialisation.
Coming at a time when Nigeria is intensifying efforts to diversify its economy away from oil dependence, stakeholders say the success of this alliance could mark a turning point — shifting the country from being one of Africa’s largest automotive consumption markets to an emerging centre of production, innovation, and regional trade.
Business
Nigerian Equities Post World’s Second-Best Dollar Returns in 2026, Recover $21bn

Nigerian Equities Post World’s Second-Best Dollar Returns in 2026, Recover $21bn
Nigerian equities have emerged as one of the best-performing stock markets globally in 2026, delivering the world’s second-best dollar returns after years of currency-driven losses and weak investor sentiment. The local market has risen 31 percent in dollar terms this year, helping investors recoup about $21 billion in market value lost following the sharp naira devaluation in 2024.
Market capitalisation on the Nigerian Exchange Group has climbed to approximately $84 billion, representing a 58 percent increase from levels recorded before the currency collapse. According to Bloomberg, Nigeria’s benchmark equity index has surged 31 percent year-to-date, significantly outperforming global peers. The rally far outpaces the 11 percent gain in the broader emerging-market index and the 6.4 percent advance recorded by frontier-market stocks.
Analysts attribute the sharp rebound to a combination of stronger corporate earnings, exchange-rate stability, and renewed investor confidence following wide-ranging economic reforms. Olabode Williams, an analyst at SBG Securities Ltd, said companies hardest hit by the naira’s earlier collapse have now stabilised their balance sheets and returned to profitability. He noted that investors are increasingly pricing in growth as corporate fundamentals improve, adding that Nigerian equities are becoming more attractive to both local and foreign investors after years of underperformance.
READ ALSO:
- Ramadan Begins in Nigeria as Sultan Confirms Crescent Sighting
- Deadlock at National Assembly as House Snubs Electoral Act Bill Meeting on E-Transmission Clause
- Maikori Accuses Ex‑Governor El‑Rufai of Persecution Over 2017 Tweet
The rally has also been supported by a firmer naira, which has appreciated by more than seven percent against the dollar in 2026, ranking as the world’s second-best performing currency among those tracked by Bloomberg. The currency rebound has strengthened dollar-based equity returns and helped reverse losses triggered by earlier exchange-rate volatility.
Foreign participation has increased sharply alongside the rally. Data from the Nigerian Exchange Group shows that non-Nigerian trading in local equities reached a 19-year high in 2025. Transactions by foreign investors tripled to ₦2.65 trillion ($1.97 billion) from ₦852 billion in the previous year, reflecting renewed global appetite for Nigerian risk assets.
Market analysts believe the rally could extend further if major listings materialise. Gloria Fadipe, an analyst at CSL Stockbrokers Ltd, a unit of FCMB Group Plc, said the market could exceed $100 billion in valuation this year if large-scale listings proceed. She noted that potential listings of Dangote Refinery and Dangote Fertiliser could deliver capital gains of up to 34 percent while deepening market liquidity.
The rebound comes amid broader macroeconomic reforms introduced by Bola Tinubu, including the unification and liberalisation of the foreign-exchange market. While the reforms initially triggered volatility and inflationary pressure, economists say they are restoring policy credibility, improving capital inflows, and repositioning Nigerian assets for sustained long-term growth.
Nigerian Equities Post World’s Second-Best Dollar Returns in 2026, Recover $21bn
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoSaudi Arabia Confirms Sighting of Ramadan Crescent, Fasting Begins Wednesday
-

 metro2 days ago
metro2 days agoLagos Woman Shares Ordeal After Alleged Rape, Sparks Nationwide Outcry
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoRamadan Begins in Nigeria as Sultan Confirms Crescent Sighting
-

 metro2 days ago
metro2 days agoSeven Killed in Horrific Crash at Ota Toll Gate
-

 International17 hours ago
International17 hours agoCanada Opens New Express Entry Draw for Nigerian Workers, Others
-

 metro3 days ago
metro3 days agoDeadlock at National Assembly as House Snubs Electoral Act Bill Meeting on E-Transmission Clause
-
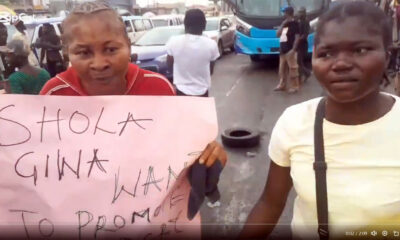
 News2 days ago
News2 days agoKorope Drivers Shut Down Lekki–Epe Expressway Over Lagos Ban (Video)
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoRamadan Health Tips: Six Ways to Stay Hydrated While Fasting















