Health
Reps, NAFDAC lift ban on sale of sachet alcoholic beverages

Reps, NAFDAC lift ban on sale of sachet alcoholic beverages
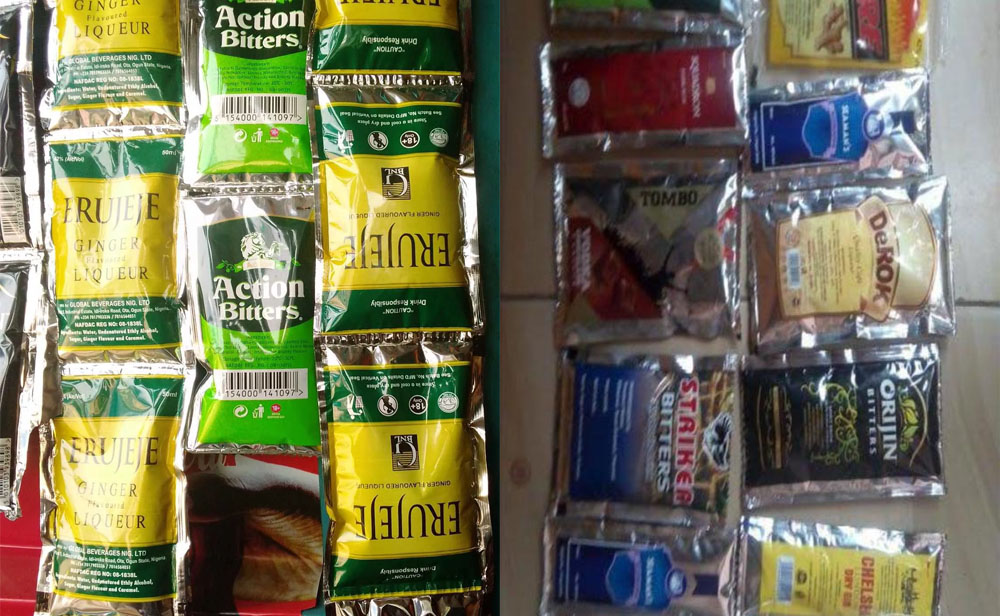
The House of Representatives and the National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC) have decided to lift the ban on the sale and consumption of sachet alcoholic beverages in the country temporarily.
This decision will remain until the economy recovers fully. NAFDAC initially banned these beverages due to concerns about drug abuse, especially among young Nigerians.
On February 7, 2024, the House mandated its committee to investigate the ban.
The decision to lift the ban temporarily followed a meeting between the House Committee and NAFDAC officials, as announced by Deputy House spokesman Philip Agbese.
READ ALSO:
- Sex-starved husband cries for help as wife allegedly threatens him for dating another woman
- Kenyan policeman shoots magistrate in open court
- Stay away from rotten tomatoes, pepper; doctor warns Nigerians
He said, “We all agreed at the meeting that at a certain stage in history, we must move on with our counterparts across the globe. Nevertheless, at the moment, we agreed with NAFDAC that there would be a temporary lifting of the ban until the economy regains its strength.”
Speaking on how the decision was arrived at, Agbese who represents Ado/Ogbadigbo/Okpokwu Federal Constituency, Benue State, said, “We had engagements with stakeholders, including NAFDAC and the organised private sector involved. Resolutions were reached at that meeting based on the submissions made by the stakeholders, civil society organisations and other interested parties.
“Part of the recommendations before the parliament was that the ban was not timely given the current economic realities and coupled with the fact that the five-year moratorium granted by NAFDAC to the private sector, the advent of COVID-19 and other economic realities we are facing today did not permit the operators in the industry to comply with their terms.”
Reps, NAFDAC lift ban on sale of sachet alcoholic beverages
Health
Just In: Nigeria receives 846,000 malaria vaccine doses

Just In: Nigeria receives 846,000 malaria vaccine doses
Nigeria has received 846,000 doses of a groundbreaking malaria vaccine from development partners to reduce the country’s high incidence of the disease, especially among children and other vulnerable groups.
Prof. Muhammad Pate, Coordinating Minister of Health and Social Welfare, announced during the event on Thursday in Abuja that the vaccines were expected to play a pivotal role in lowering malaria-related deaths.
The News Agency of Nigeria (NAN) reports that large clinical trials in Africa proved the vaccine, RTS,S/AS01 (Mosquirix) as effective in reducing contracting malaria cases and mortality among young children.
Nigeria is the third African country to introduce the vaccine, following Ghana and Kenya, which began using it in 2023.
Malaria affects 97 per cent of Nigeria’s population. Its transmission occurs year-round in southern regions and lasts up to three months in the northern regions.
The primary malaria vectors are Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles gambiae, with Anopheles funestus playing a secondary role in some areas.
The vaccines come as Nigeria intensifies efforts to reduce malaria-related deaths under the National Malaria Strategic Plan (NMSP) 2021–2025.
Pate said the vaccine would significantly boost the country’s ongoing malaria elimination efforts.
“Our target is to prioritize regions most affected by malaria, particularly in rural areas where access to healthcare is limited,” he said.
He also said the vaccine rollout would begin in high-burden regions before expanding nationwide.
According to him, global health partners, including WHO, UNICEF, and Gavi, are providing technical and financial support to ensure the successful implementation of the vaccine.
READ ALSO:
- Biden okays $4.5bn student debt relief as vote nears
- Don Jazzy raises Verydarkman NGO with N100m
- EFCC calls 15th witness in Fayose fraud trial
Just In: Nigeria receives 846,000 malaria vaccine doses
Health
Cholera ravages 28 LGs in Kano, kills 45
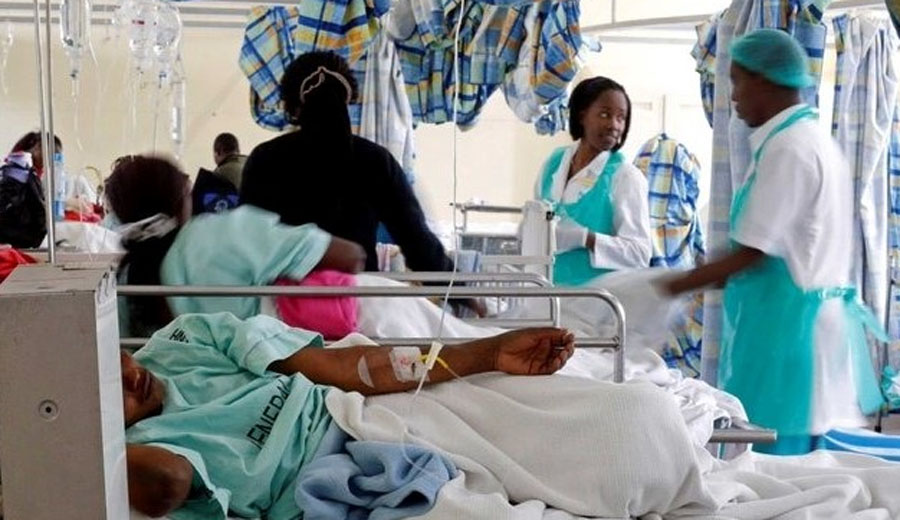
Cholera ravages 28 LGs in Kano, kills 45
The Coordinator of the Kano State Centre for Disease Control (KNCDC), Prof. Muhammad Adam Abbas, has revealed that a recent cholera outbreak has claimed 45 lives across 28 local government areas in the state.
He stated this on Tuesday at a retreat organised by the Kano State’s Ministry of Health in Kaduna.
According to Prof. Abbas, cholera thrives in environments with poor sanitary conditions, and maintaining high standards of personal and food hygiene is vital in combating its transmission.
READ ALSO:
- Police in Imo burst robbery gang terrorising Owerri
- Ahead Ondo poll, PDP demands removal of INEC commissioner
- Pro-Fubara lawmakers react to Amaewhule-led faction declaring their seats vacant
He advised that frequent handwashing, maintaining a clean environment, thoroughly washing fruits and vegetables and proper food storage are essential preventive measures.
He also highlighted the increased risk during the rainy season, as running water can wash contaminants, including dirt and faeces, into low-lying wells.
To mitigate this, he recommended building parapet embankments around wells to prevent contamination.
Prof. Abbas further noted that the government is taking proactive steps to control the outbreak, including chlorinating water sources in communities with poor sanitation and those affected by the disease.
Cholera ravages 28 LGs in Kano, kills 45
Health
Breakthrough in wound healing, electric suture creates excitement

Breakthrough in wound healing, electric suture creates excitement
A new type of suture that combines electrical stimulation with traditional suturing methods has been developed.
It has been demonstrated that this mechanoelectric suture, which is constructed from biodegradable materials and generates electric fields in response to movement, significantly accelerates wound healing and lowers the risk of infection.
This innovative approach could revolutionise wound closure procedures and offer patients a faster and safer healing process.
In an experiment in rats, the new strong, flexible thread hastened wound healing by transforming muscle movement into electricity, researchers report in Nature Communications.
According to materials scientist Chengyi Hou of Shanghai’s Donghua University, the substance “could change how we treat injuries” if it is finally shown to be safe for use in humans.
READ ALSO:
- Rumour of Mohbad’s widow Wunmi expecting another child sparks shocking reactions
- Bobrisky: I was treated badly during my visit to EFCC office, says Verydarkman (VIDEO)
- Kano: Lebanese jailed 14 years for sexually exploiting two teenage girls
Although prior methods depended on large external batteries, researchers already knew that applying electricity to sutures helped accelerate the healing process. The body provides the energy for the new sutures.
The thread is composed of magnesium, a metal that the body may eventually absorb, and biodegradable polymers. The central layer of the thread rubs against the outer shell when the muscles around the sutures contract and relax, which transfers electrons to the shell and produces electricity.
Hou and colleagues used the thread’s electrical stimulation to treat artificial wounds in lab dishes. After 24 hours, fibroblasts, which are critical to healing, reduced the wound area from 69 percent to 11 percent. Untreated artificial wounds reduced in size from 69 percent to 33 percent after 24 hours.
Rodents treated with electrical sutures recovered faster and were less likely to acquire infections than rats treated with regular sutures or left untreated. Next, the team intends to try the sutures on bigger animals.
Breakthrough in wound healing, electric suture create excitement
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoFIRS announces recruitment of young graduates
-

 metro3 days ago
metro3 days agoUpdated: Army says reports of COAS Lagbaja’s death fake news
-

 metro2 days ago
metro2 days agoOluwo chased me out when I visited him – Ooni (VIDEO)
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoOsinbajo traitor, can’t talk about integrity – Reno Omokri
-

 metro2 days ago
metro2 days agoFani-Kayode: How my aide died in hotel after attending church
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoWe’re settling out of court with NNPC, others — Dangote
-

 metro2 days ago
metro2 days agoBREAKING : DSS replaces Tinubu’s chief security officer
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoYou can’t overrule Supreme Court on LG autonomy – Klinsmann tells Soludo