International
Ukraine asks UN court to end Russia invasion

Ukraine will square off with Russia at the UN’s top court on Monday, with Kyiv asking judges in The Hague to order Moscow to immediately halt its invasion.
Kyiv lodged an urgent case at the International Court of Justice (ICJ) on February 27, saying that Russia had illegally justified its war by falsely alleging genocide in Ukraine’s Donetsk and Lugansk regions.
Ukraine alleges that it is Russia that is planning “acts of genocide” in the offensive launched by President Vladimir Putin on February 24.
Kyiv has asked the court to take provisional measures ordering Russia to “immediately suspend the military operations”, pending a full judgment that could take years.
“Ukraine emphatically denies that acts of genocide have been committed”, Kyiv’s application to the court said.
“Russia thus expressly bases its ‘special military operation’ — in fact a full-scale, brutal invasion of Ukraine — on an absurd lie.”
In an unusual step, ICJ President Joan Donoghue issued an “urgent communication” to Russia on March 1 asking it to “act in such a way” that any order should take effect quickly.
READ ALSO:
- Arrested randy husband seeks forgiveness for raping in-law for three years
- Five men digging pit trapped, buried alive in Kano
- Tears as rain wreaks havoc in Ibadan
The two-day hearing at the ICJ’s Peace Palace headquarters will begin with Ukraine speaking on Monday at 0900 GMT. Russia is slated to reply on Tuesday.
It was not clear how Moscow would formally contest Ukraine’s application and the Russian embassy in The Hague did not respond to a request for comment.
In another blow to Moscow’s case, its legal team will be weakened by the resignation of one of its long-time French lawyers, Alain Pellet.
“Lawyers can defend more or less questionable causes,” Pellet said in an open letter.
“But it has become impossible to represent in forums dedicated to the application of the law a country that so cynically despises it,” he said.
The ICJ was set up after World War II to rule on disputes between UN member states, based mainly on treaties and conventions.
Its rulings are binding but it has no real means to enforce them.
– ‘Offensive and ironic’ –
Experts said Ukraine’s effort to drag Russia to the world court over the invasion could have symbolic value, though it was unclear if Moscow would heed any order.
“It remains to be seen what will happen at the provisional measures stage but my bet is that the court will find that it has prima facie jurisdiction,” Cecily Rose, assistant public law professor at Leiden University, told AFP.
“Not that Russia is likely to comply but still — rhetorically and symbolically there is some power to this,” added international public law professor Marko Milanovic, writing in the European Journal of International Law.
This case hinges on the 1948 UN Convention on Genocide, to which both Ukraine and Russia are parties.
The ICJ was already dealing with a dispute between the two countries dating back to Russia’s 2014 annexation of Crimea and support for pro-Moscow rebels in Donetsk and Lugansk.
But now, Kyiv says that Russia “has falsely claimed that acts of genocide have occurred in the Lugansk and Donetsk” regions and has invaded on that basis.
“Russia’s lie is all the more offensive, and ironic, because it appears that it is Russia planning acts of genocide in Ukraine,” Kyiv’s application said.
The case is separate to a Ukraine war crimes investigation launched by the International Criminal Court (ICC), a different tribunal also based in The Hague.
The ICC’s chief prosecutor Karim Khan on Wednesday announced he was going ahead with an investigation into alleged war crimes and crimes against humanity committed in Ukraine since Moscow’s invasion.
AFP
International
Gaza: Iran begins talks with S’Arabia, Egypt as Israel renews attacks

Gaza: Iran begins talks with S’Arabia, Egypt as Israel renews attacks
Iran’s Foreign Minister Seyed Abbas Araghchi on Saturday exchanged views with his Saudi Arabian and Egyptian counterparts on Israel’s renewed attacks on Gaza.
In a phone conversation with Saudi Foreign Minister Faisal bin Farhan Al Saud, Araghchi strongly condemned Israel’s attacks in Gaza, and urged other countries in the region to take collective action, said the Iranian Foreign Ministry in a statement.
For his part, Faisal reaffirmed Saudi Arabia’s condemnation of Israeli aggressions and emphasized regional coordination to prevent further escalation.
READ ALSO:
- Disregard court order against Rivers Administrator, says Fubara’s aide
- Three killed,15 injured in U.S. park shooting
- Why governors’ forum is silent on Rivers emergency, by DG
In a separate phone call with Egyptian Foreign Minister Badr Abdelatty, Araghchi condemned Israel’s renewed attacks on Gaza as well as obstruction of humanitarian aid delivery to the Palestinian coastal enclave “in flagrant violation” of the ceasefire agreement with Hamas.
The Egyptian foreign minister underscored the need for consultations and diplomatic efforts to prevent further escalation.
Both Egyptian and Iranian ministers agreed to maintain consultations on regional developments.
Gaza: Iran begins talks with S’Arabia, Egypt as Israel renews attacks
Xinhua
International
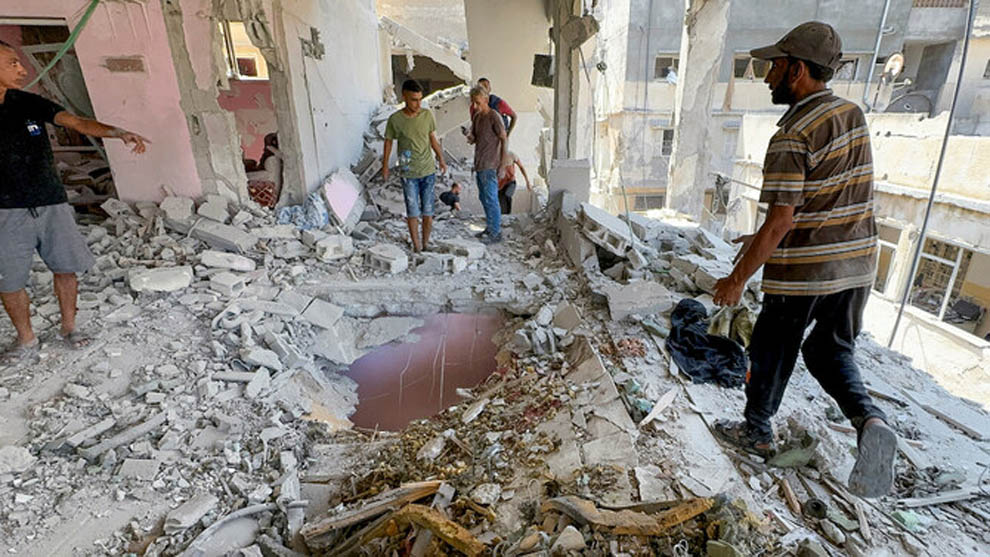
Three killed,15 injured in U.S. park shooting

Three killed,15 injured in U.S. park shooting
Three people were killed and 15 others injured in a shooting at Young Park in Las Cruces, New Mexico, on Friday night, police said.
The violence erupted during an unauthorised car show that had drawn around 200 people.
Las Cruces Police Chief, Jeremy Story, said officers arrived at the scene around 10 p.m. to find chaos, with 50 to 60 shell casings, all from handguns, scattered across the park.
The shooting involved multiple weapons and appeared to stem from an ongoing conflict between two groups, Story said, adding that several bystanders were caught in the crossfire.
The deceased were identified as two 19-year-old men and a 16-year-old boy. The names of the victims, including those injured, have not yet been released.
The wounded, ranging in age from 16 to 36, were either treated at the scene or taken to area hospitals.
Las Cruces Fire Chief Michael Daniels said seven victims were treated at the spot, including two who died due to their injuries.
Eleven others were transported to hospitals in Las Cruces or the University Medical Center of El Paso, a regional trauma center. By Saturday, four had been released, while seven remained hospitalised. The conditions of the remaining four were unclear.
READ ALSO:
- Why governors’ forum is silent on Rivers emergency, by DG
- Senate didn’t get 2\3 majority for Tinubu emergency rule in Rivers –Tambuwal
- FG destroys another 200 containers of expired drugs
The police are working with the New Mexico State Police, Doña Ana County Sheriff’s Office, FBI, and the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives to investigate the incident.
Authorities are asking for eye witness accounts and any video footage to help identify the suspects.
“This horrendous, senseless act is a stark reminder of the blatant disregard for law and order,” Story said, while vowing to find and hold all perpetrators accountable.
Story acknowledged that illegal car shows at Young Park have been a recurring issue and that police presence had been greater in the past. However, due to staffing shortages, there were “no units available for most of the night” on Friday.
The city has purchased surveillance technology for all its parks as part of a real-time crime center, but it has not yet been installed.
Las Cruces City Councilor and Mayor Pro Tem Johana Bencomo, expressed her grief over the tragedy.
“A tragedy like this feels like a nightmare just waiting to come true at any possible moment,” she wrote on Instagram.
Las Cruces, located along the Rio Grande in southern New Mexico, is about 40 miles north of the U.S.-Mexico border.
Police remained at the scene Saturday, keeping the area closed to traffic as the investigation continued.
The incident has intensified discussions about crime and gun violence in New Mexico.
New Mexico Governor, Michelle Lujan Grisham recently signed legislation imposing harsher penalties for crimes like vehicle theft and fentanyl trafficking while also banning devices that convert guns into automatic weapons.
The state also expanded its red-flag gun law and increased funding for addiction and mental health treatment.
The New Mexico Senate held a moment of silence late Friday in response to the tragedy.
Three killed,15 injured in U.S. park shooting
International
Canada offers cybersecurity training with job placements for immigrants

Canada offers cybersecurity training with job placements for immigrants
The Canadian government, in collaboration with private sector partners, is offering a cybersecurity training programme in Calgary designed to support immigrants in securing employment in the growing tech industry.
The initiative provides hands-on learning and job placement opportunities in one of 16 entry-level cybersecurity roles. Participants will earn industry-recognized micro-credentials, equipping them with the skills needed to launch their careers.
READ ALSO:
- Rivers: Tinubu acted to save state, economy, says Karimi
- Oluwo accuses Ooni of plotting to dethrone him
- Lagos man stabs security guard for stopping his sex romp
Funded by the Alberta Ministry of Jobs, Economy and Trade, the programme is delivered in partnership with ReTrain Canada and Manpower Canada. The 12-week training session, scheduled for March, will run Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 4 p.m.
Through this initiative, participants will gain expertise in cybersecurity fundamentals, encryption techniques, and applied penetration testing—all at no cost—while also receiving practical work experience to enhance their employability.
Canada offers cybersecurity training with job placements for immigrants
-

 metro2 days ago
metro2 days ago‘We’re not hiring,’ NNPC denies viral recruitment adverts
-

 metro1 day ago
metro1 day agoNatasha: Court blocks recall attempt, stops INEC
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoOdegbami speaks on Osimhen breaking his 44-year goals record
-

 metro2 days ago
metro2 days agoMore trouble brews in Rivers as Ijaw congress considers self-determination option
-

 Entertainment1 day ago
Entertainment1 day agoI didn’t snatch Asake’s mother from her husband -Musibau Alani
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days ago2026 WCQ: Super Eagles move up to third place with 2-0 win in Rwanda
-

 metro1 day ago
metro1 day agoBoko Haram attacks military base in Adamawa
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoOsimhen breaks Odegbami’s Eagles goal record